A Conceptual Study on Vatarakta w.s.r. to Gouty Arthritis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ayushdhara.v11i3.1560Keywords:
Vatarakta, Gouty Arthritis, Pada moola, Ayurveda, hyperuricemia, SandhishoolaAbstract
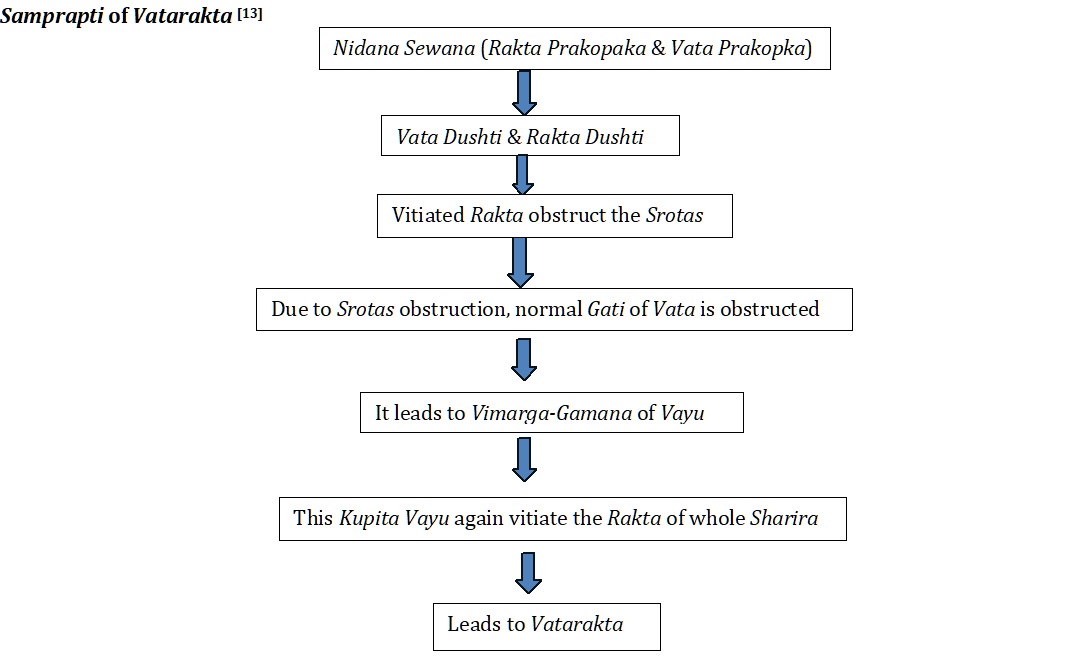
The wellbeing of an individual depends on his/her diet and lifestyle. The rapid development and modernisation in India are causing serious health problems and Vatarakta is one of them. Vatarakta, is described under Vatavyadhis by different Acharya’s. The vitiated Vata and Rakta causes this disease, hence called Vatarakta. Gout is an inflammatory disease caused by deposition of Mono-Sodium Urate (MSU) crystals in and around synovial joints. Recent reports of prevalence and incidence of gout vary widely but ranges from prevalence of 1-2%, with greater than 5:1 male preponderance. It is imperative to comprehend complexities of Vatarakta in order to accurately diagnose and treat it, considering its increasing occurrence worldwide and the substantial influence, it has affected individuals’ quality of life. Methods: After a thorough literary review, focusing on classical Ayurvedic texts, alongside recent research articles and reviews. The gathered information was analysed to present cohesive narrative on the Niadana, Samprapti and Chikitsa of Vatarakta. Results: Vatarakta is a result of aggravated Vata Dosha and impaired Rakta Dhatu, leading to severe pain, inflammation, and joints deformity. The disease progression is influenced by dietary habits, lifestyle factors, and genetic predisposition. Its treatment involves a multi-factorial approach, including Shodhana, Shamana, dietary regulations, and lifestyle modification. Conclusion: The Ayurvedic perspective on Vatarakta offers a holistic approach in understanding and managing the disease, emphasizing the balance of bodily Doshas, detoxification, and rejuvenation. Integrating Ayurvedic principles with modern medical practices may provide a comprehensive treatment for Vatarakta.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 AYUSHDHARA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


