Antifungal Activity of Bhurjah (Betula Utilis d. Don) Bark in Human Pathogenic Fungi
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ayushdhara.v11i3.1576Keywords:
Antifungal activity, Bhurjah, Betula utilis D.Don, Birch oil, Inhibition zone, MICAbstract
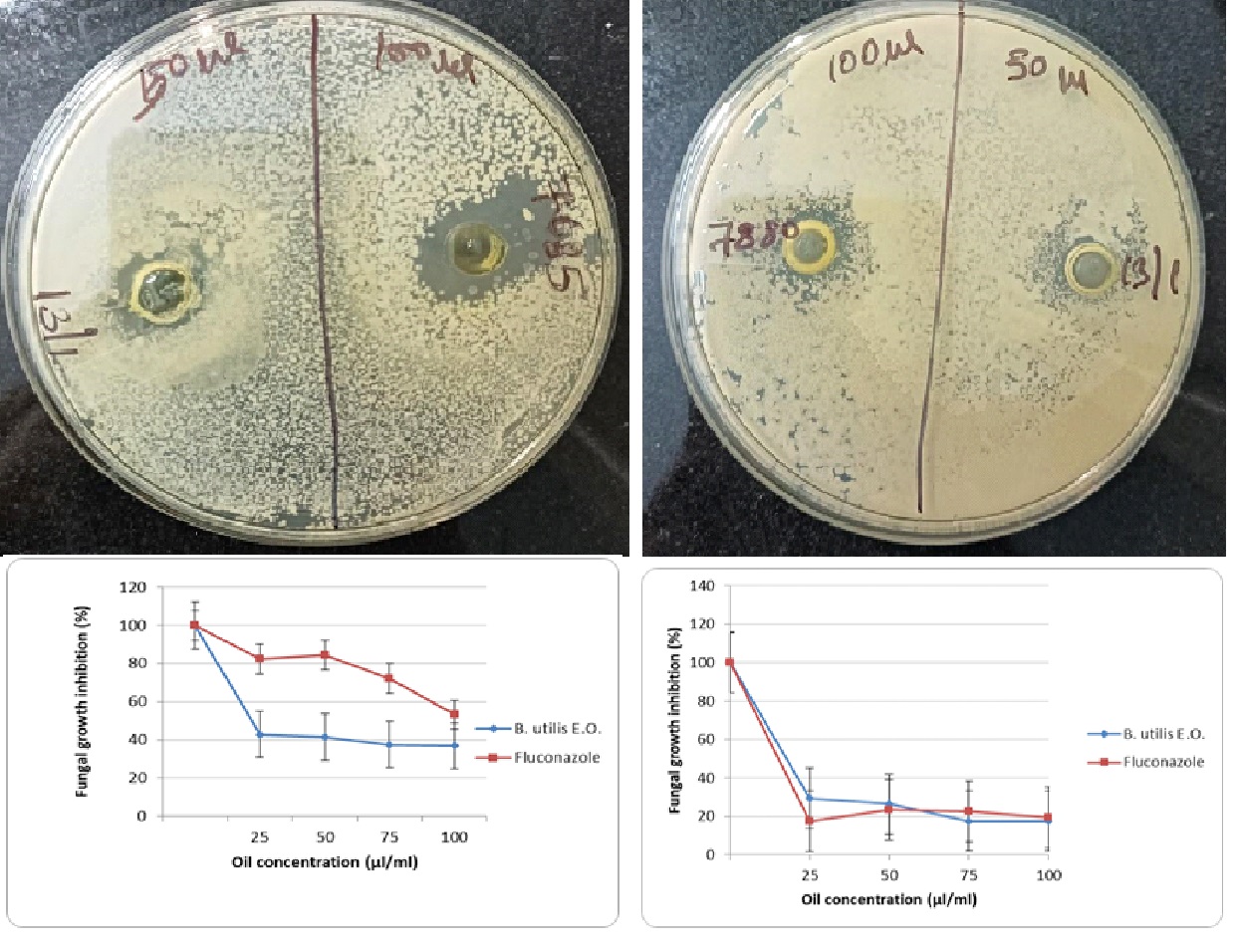
Aim: To evaluate the antifungal activity of Bhurjah (Betula utilis D.Don) bark against six fungal strains. Water extract, alcohol extract of bark and essential oil (Birch oil) were screened against six fungal strain Trichophyton rubrum (7859), Epidermophyton floccosum (7880), Microsporum fulvum (7685), Aspergillus flavus (2590), Actinomucour elengi (963) and Candida albicans at four different concentrations (25µl, 50µl, 75µl, 100µl) using “Agar well diffusion method”. The MIC was tested using micro-PDA dilution method at concentrations ranging from (25µl, 50µl, 75µl, 100µl). Bhurjah essential oil showed significantly more inhibitory activity than fluconazole in case of 7880 (p value <0.05) and almost similar inhibitory activity as fluconazole in case of 7685 (p value >0.05). Bhurjah essential oil is shown to be effective against the growth of both M. fulvum with MIC value of 2.5% (v/v) and E. floccosum with MIC value of 2.5% (v/v) as determined by microbroth dilution. Bhurjah essential oil showed antifungal activity against two fungal strains E. floccosum (7880), M. fulvum (7685). Therefore Bhurjah essential oil can be used as antifungal agents for dermatophytosis causing strains i.e. E. floccosum (7880), M. fulvum (7685).
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 AYUSHDHARA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


