Comparative Anti-Microbial Efficacy Evaluation of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Medicinal Plants in Vulvovaginitis: An In-Vitro Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ayushdhara.v12i2.1984Keywords:
Antimicrobial activity, Ayurveda, Extract, Vulvovaginitis, Zone of inhibitionAbstract
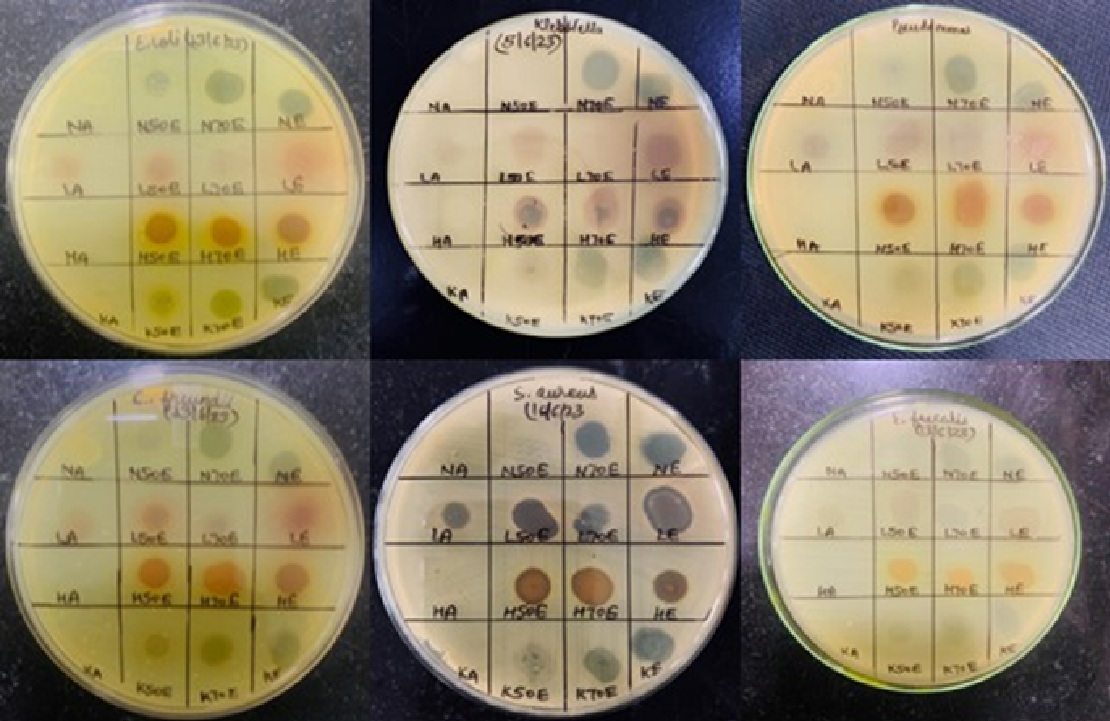
Vulvovaginitis is infection of vulva and vagina where bacteria are the most common etiological agent. Treatment of vaginal infection should aim not only to eradicate pathogenic organisms, but also at supporting the normal vaginal microflora. Most of the antibiotics used for its treatment are associated with development of resistant micro-organisms and drug-induced side-effects. So, an attempt has been made to investigate in-vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing of medicinal plant extracts for better therapeutic outcome. Aim and objective: To screen out antimicrobial activity of hydroalcoholic extract of Azadirachta indica, Symplocos racemosa, Curcuma longa and Pongamia pinnata with an objective to treat vaginal infections. Material and method: This in-vitro study evaluates antimicrobial activity by measuring zone of inhibition against standard ATCC bacterial strains responsible for vulvovaginitis using spot test assay. Result and Discussion: C. longa and S. racemose exhibited strongest antimicrobial activity for gram-negative bacteria and gram-positive bacteria respectively. Among different extracts, 70% ethanolic extract of A. indica and P. pinnata, ethanolic extract of S. racemosa and 50% ethanolic extract of C. longa exhibited the highest antimicrobial activity. Conclusion: Hence, these plants can be used to treat vulvovaginitis that may serve as lead in the development of new potent herbal antibiotics to which pathogen strains are not resistant.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 AYUSHDHARA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


