The Management of Schizophrenia Progressed from Substance-Induced Psychosis with a Selected Ayurvedic Protocol
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.47070/ayushdhara.v12i2.2058Keywords:
Schizophrenia, Substance use, Unmada, AyurvedaAbstract
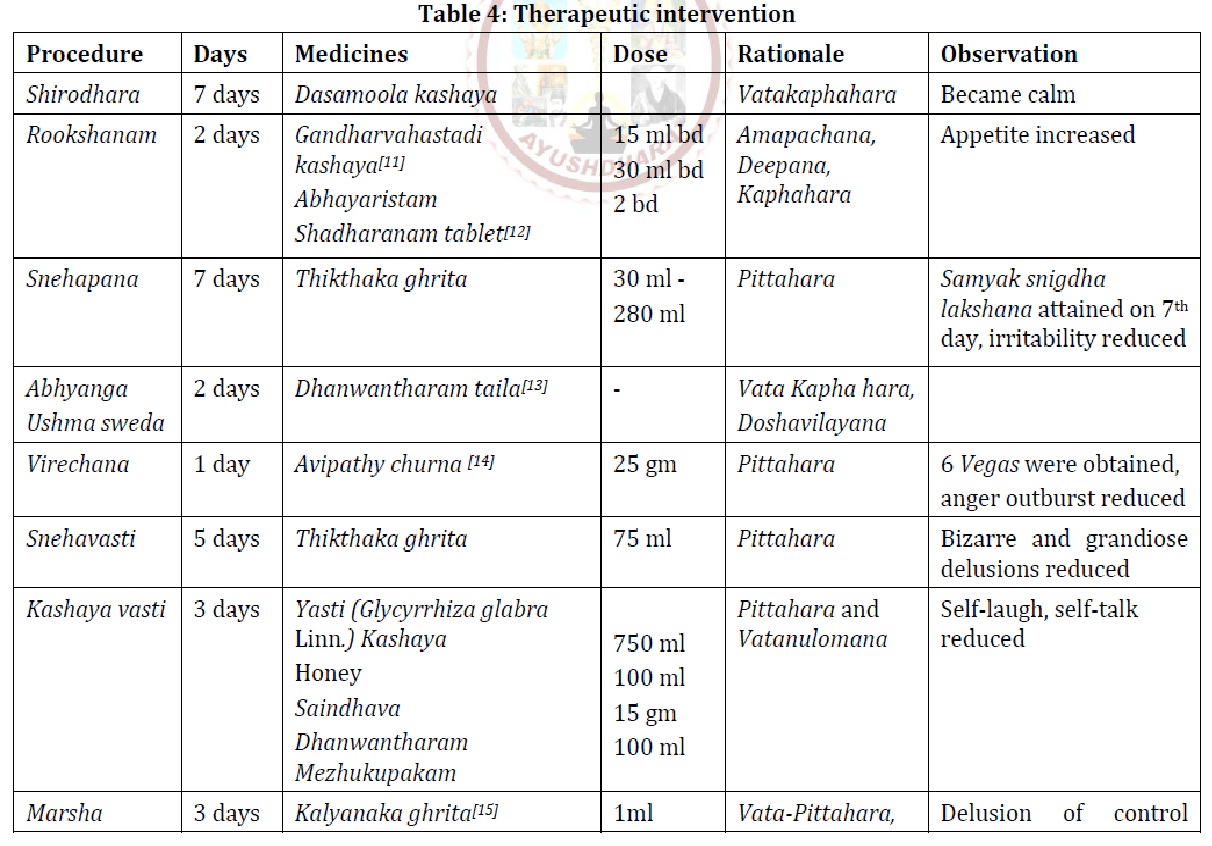
Schizophrenia, which progresses from substance-induced psychosis (SIP), is a psychiatric condition in which an initial substance-related psychotic episode develops into a chronic psychotic disorder. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), defines SIP as a state of delusions or hallucinations triggered by substance use or withdrawal. Studies suggest that 11–46% of individuals with SIP may progress to schizophrenia, with cannabinoids, stimulants, and alcohol being the most common triggers. However, SIP remains underdiagnosed, and its progression to schizophrenia is not well characterized. This case illustrates the importance of Ayurvedic management of a patient having psychotic symptoms (auditory hallucinations, multiple bizarre delusions) that arose from SIP having h/o substance use (alcohol, cigarettes, cannabis) from the last 10 years. Ayurveda classifies psychotic disorders under Unmada and offers a holistic treatment approach that includes internal medicines and panchakarma therapies. 33 days of IP management which include Shirodhara, Rookshana, Snehapana, Virechana, Yoga vasti, Nasya, shiropichu and Dhoopana were followed along with Shamana medication. A positive and negative syndrome scale was used for assessment before and after the treatment. The PANSS scores significantly decreased from 81 to 49 post-treatment, patient reported decrease in substance craving, and positive psychotic symptoms improved with no adverse reactions. This case provides the evidence of effect of ayurvedic management on schizophrenia progressing from substance-induced psychosis and offers an alternative and safe option from conventional medication.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 AYUSHDHARA

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


